Bypass VPN Blocks Using the Power of Obfuscation
Internet Enemies like China, Iran, Russia, Syria, and Egypt are now focusing on VPN blocking – a technique for halting encrypted protocol tunneling that keeps netizens anonymous.
Online services such as Hulu, Netflix, and BBC iPlayer also follow suit, preventing access to users around the world using the VoDs with a VPN service to unblock geo-restricted content.
It was bad enough that users had to watch out for logging policies and leak issues, but now they also need to ensure the VPN they choose is safe from such blockages!
After all, the entire purpose of using a VPN is to keep your identity anonymous, even in countries that are generally strict on making certain information available to the public.
This is where a feature called “Obfuscation” comes in handy – a.k.a. “StealthVPN” by most providers in the marketplace, which allows for the bypassing of VPN blocking.
So, this BestVPN.co guide is for the privacy-conscious users living in “Internet Enemy” locations. In here, I will provide in-depth information about obfuscation, how it works, and its many uses!
VPN Obfuscation Detailed Guide 2019
What is Obfuscation?
In layman terms, obfuscation involves the usage of different technologies and programming code to make something difficult to understand.
Various different products/services use obfuscation to protect intellectual property by preventing attackers from reverse engineering a proprietary software.
The process may involve code encryption, renaming variable names to meaningless labels, adding unused code to an application library, or stripping out revealing metadata.
Obfuscators are typically utilized for automatically converting straight-forward source code into a program that works like originally intended, but just harder to read/understand.
This is why obfuscation is such a reliable method for hiding VPN traffic, disguising traffic to look like regular unencrypted traffic, allowing users to bypass VPN blocks.
It does so by hiding all sent and received requests behind the standard HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encryption, like when connecting to a banking website via port 443.
How Does a VPN Use Obfuscation?
VPNs allow your internet connection to pass through a secure and encrypted tunnel. They also hide your location by giving you a new IP address based on the server you connect to, keeping you anonymous from the prying eyes of government agencies, cybercriminals, and copyright hunters.
This is one reason why these tools are so popular for digital nomads and the common man, where there is blocking of IP addresses, ports, DNS, and protocols. However, VPNs are a target themselves in countries that use Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) for blocking targeted apps/protocols.
Since DPI’s act based on the type of packet, not the port number, you cannot receive complete protection from these bans until you use “Obfuscation”. Below you can see a diagram that highlights how a normal connection using the OpenVPN Protocol looks like.
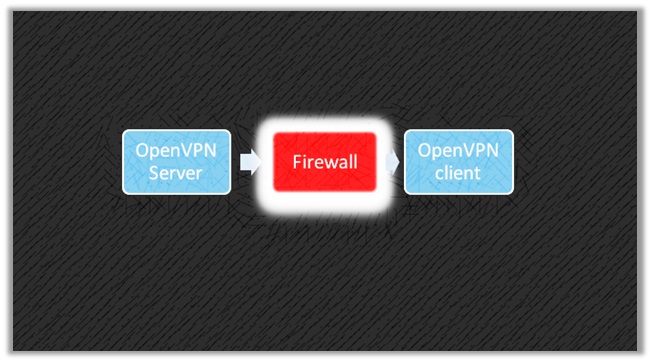
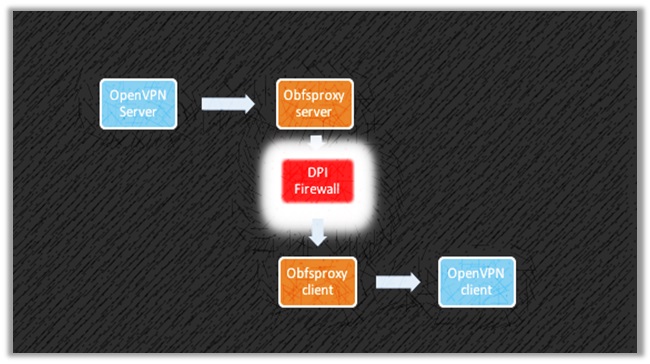
Obfuscation operates quite differently and uses pluggable transports to proxify the traffic into obfuscated tunnels, which are more difficult to identity or pass through.
Most VPNs utilize the OpenVPN protocol for implementing “XOR Obfuscation” a.k.a. OpenVPN Scramble, which proves highly useful against deep packet inspection (DPI).
OpenVPN Scramble uses the XOR Encryption Algorithm for defeating advanced VPN blocks used by countries like China, Iran, Russia, Syria, and Egypt.
The XOR Cipher
Pronounced as “Ex-or”, XOR – stands for Exclusive or. It is a type of mathematical operation that uses the XOR cipher, which replaces each alphanumeric in a string, fed into another number.
Since the algorithm is reversible, you can feed the output string back into the same cipher, ending up with the original string and the cipher removed.
This kind of cipher used by XOR is also known as an “Additive Cipher” or ROT13, which clever technicians use for creating secret messages.
How Effective is Openvpn Scramble (XOR Obfuscation)?
When you connect to a server that uses XOR Obfuscation, the OpenVPN-encrypted data with the XOR ciphers make it harder for DPIs and systems like “The Great Firewall” to identity.
This is one of the reasons why it has received quite the notoriety in the marketplace of VPNs, because it also adopts an easy implementation technique.
You can even find malware developers using obfuscation to hide their nasty bits of code from anti-malware detection. They use a 1-byte value that plays the role of a “key”.
The code obfuscated then encodes into every byte of data, XOR’ing each byte with the selected key. However, it is possible to use longer keys too, which most VPNs do utilize.
Typically, the effectiveness of XOR for scrambling data completely relies on how random of a key it uses, hence why it is so effective – which can also be verified by its widespread use.
You can even conduct a test. Turn on a regular VPN and test it on Wireshark. The traffic will be seen as OpenVPN. With Obfuscation activated, Wireshark will no longer identify the traffic as OpenVPN.
How VPN Data Transforms into ‘Obfuscated’ Packets
When you connect to an “Obfuscated Server” or activate the “StealthVPN” feature, it pushes forward a mechanism that makes it impossible to block VPN tunnels.
Bear in mind though the process may differ depending on the type of Obfuscation. Since most VPNs use the XOR Obfuscation method, I have highlighted the steps for this particular feature:
Step #1 – Activating Regular OpenVPN Encrypted Connection
OpenVPN data packets consist of two parts: The Header and The Payload. The former has packet identification and routing information. The latter is the encrypted portion of those data packets, forwarded by the VPN server to the relevant web address.
Since the header has identifiable information for the source of a packet, it also includes the port number (#) along with data that identifies the packets as “OpenVPN”. This is what typically allows VPN Block systems and Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) from identifying that you are using a VPN.
Step #2 – Eliminating VPN Data from the Header
The provider will now use “XOR Obfuscation” to remove all the Metadata from the packet header, transforming it into meaningless information, to preventing identification of a VPN protocol.
Think of it as similar to looking at a car, but someone removed the number plate, engine number, branding, and other labels – making it impossible to identify the model/make.
Step #3 – Disguising the VPN Data as HTTPs
Step 3 is where the role of “XOR Obfuscation” ends and the process of disguising begins. The process involves transforming the “obfuscated” traffic into HTTPS encrypted web traffic.
In order to do this, providers will use two prominent characteristics of https data: SSL/TLS Encryption and Port #443, allowing users to slip through firewalls undetected.
SSL/TLS Encryption
The obfuscated OpenVPN data packets now go through a second layer of encryption, which uses the SSL or TLS protocol. This may vary though depending on the VPN service.
Port #443
After adding an extra layer of encryption, the VPN data is assigned to port #443 (used by HTTPS traffic), making the packets virtually similar to regular HTTPS data, which is impossible to block!
Controversy about XOR Obfuscation
There is no doubt in the fact that XOR Obfuscation is highly effective in boosting your anonymity online, protecting you against government efforts to block OpenVPN traffic.
It is more definitely complicated to identify VPN traffic when integrating XOR Obfuscation, but some argue that it may not always deliver such effectiveness.
This is why the openvpn_xorpatch has been declined implementation in any official version of OpenVPN, whereas providers create their own patches to approach the issue of VPN blocks.
“We especially discourage using such an approach when there exists a far better solution, used by the TOR community. It is called obfsproxy and can be used together with OpenVPN without needing any re-compilation of OpenVPN.”
Tunnelblick’s View
Where OpenVPN GUI developers do not include the XOR Obfuscation patch, Tunnelblick still considers it a good option, due its easy implementation.
“Simply apply the patch to both the OpenVPN server and the OpenVPN client and add a single, identical option to the configuration files for each. Using obfsproxy is more complicated because it involves running another, separate program on both the server and the client.”
This ease of implementation has allowed them to include their own modified patch to all versions of OpenVPN included in Tunnelblick build 4420.
This modified patch has been through an in-depth review for security, coding, and privacy – fixing errors relating to buffer overflow, null pointer dereferences, and insufficient parameter validation.
Most VPN providers that offer “OpenVPN Scramble” use this improved XOR Patch or make similar changes to the original. OpenVPN developers, however, stick to the notion that Obfsproxy is much better.
What is Obfsproxy?
Another method of “Obfuscation”, developed by the Tor Network, Obfsproxy is a viable alternative to XOR ciphers. It wraps data into an obfuscation layer that uses pluggable transports.
These scramble the VPN (or Tor) traffic, allowing users to bypass “The Great Firewall” and circumvent geo-restrictions, all while protecting you from VPN detection and eventual blocking.
As mentioned earlier, it is also the preferred choice according to OpenVPN users, since it does not require any re-compilation of OpenVPN, which is not the case for XOR Obfuscation.
How Does Obfsproxy Work?
Similar to XOR, the Obfsproxy makes your VPN connection invisible to websites/firewalls by changing the way the flow of online traffic looks. This helps in bypassing all sorts of VPN blocks.
The privacy/security remains consistent even for firewalls that use DPI algorithms, as they classify internet traffic by determining the type of traffic i.e. VPN, SSL, HTTP, or HTTPs.
Since Obfsproxy effectively obfuscates the OpenVPN traffic to make it look like regular harmless HTTP traffic, even DPI algorithms cannot figure out whether a user is on a VPN or not.
It does so by using the “obfs2” modules that add an extra layer of encryption around the traffic, be it OpenVPN or Tor. This encryption uses a handshake process with no recognizable byte patterns.
Where Does VPN Obfuscation Come in Handy?
There are plenty use-cases for utilizing Obfuscation either in the form of XOR or Obfsproxy. For some people, who are extremely privacy-conscious, this technology is an absolute necessity.
Others want to avoid throttling or engage in p2p/file sharing activities to keep their identity hidden and anonymous to the max. However, in reality, the use of Obfuscation is much broader:
Circumventing Blocks in Countries with a VPN Ban
The usage of VPNs allows netizens like you and me to evade all government and efforts to regulate the internet, censor information, or indulge in Mass Surveillance.
Such defiance from citizens is intolerable to most intelligence agencies and countries with repressive laws that hinder freedom of speech and press.
This urges these invasive governments around the world to make efforts to block VPNs. Obfuscation helps in bypassing these bans, giving your freedom back.
Below I have listed some countries where VPN usage is illegal. You can feel assured that by activating obfuscation, you can avoid legal consequences:
China
The country stands at the forefront of banning and blocking VPN services, urging only vetted and licensed providers by the Chinese Government to continue operations.
One case even saw a Chinese man receiving a five years’ jail sentence for running a Chinese VPN. The country is among the few that demand complete control of all local ISPs.
They also use Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) to monitor all traffic entering into the Chinese Cybersphere, identifying and blocking all connections from VPN services.
UAE
The country and its famous city “Dubai” a.k.a. the Las Vegas of the Middle East may be known for its massive tourist industry. However, they are quite regressive in terms of Internet Laws.
In 2016, the UAE passed a law that made the use of a VPN punishable by a fine of up to 2 million dirham (roughly $540,000) and temporary imprisonment.
While there are certain permissible uses for VPNs, the government takes its privacy to the next level by banning VoIP calls and numerous websites, including NETFLIX.
Iran
Similar to China, Iran passed a law in 2013 that blocked access to foreign VPN services. They urged that only licensed providers from the Iranian Government can remain operational.
Selling or promoting VPN services is a crime in the country and could result in legal punishment, but the usage of such tools is still pretty much common among government officials and citizens.
Iraq
The ISIS has a strong online presence, creating all sorts of videos relating to beheading, bombings, and what not. To tackle their manifestation, the Iraq government has taken harsh steps.
This includes banning VPN services and SM platforms and instituting regular internet blackouts across the country. Though the country is free from ISIS siege, the internet restrictions remain in place.
Oman
9 years ago, the Oman Government introduced a law that makes the use of VPN services illegal. Anyone caught violating this law could be subject to a 500 riyal fine (translating to $1,300 roughly).
Enterprises that require the use of VPNs can apply for a permit to use one approved from the government, but breaking the cycle could result in a 1,000 riyal fine.
Turkey
After Erdogan came into power, the government started blocking Tor and VPN services in 2016. Turkey now uses DPI techniques, mirroring China’s ability to detect and block cloaked traffic.
If any individual is found using a VPN service, the person becomes an interest for the law enforcement, yet VPN usage is quite widespread. You can use Turkey Blocks for monitoring censorship in the country.
Belarus
Similar to other countries added to this VPN block list, the Belarusian Government also works hard in restricting access to foreign services/apps, imposing content limitations/blocks.
In 2015, the country banned the usage of VPN and Tor services, making it illegal. However, this does not stop Belarusians from doing what they want, circumventing legal/technological barriers.
Uganda
Uganda is probably one of the only few countries, where there are laws in place, which impose daily taxes on social media and other over-the-top services.
The Ugandan government has even ordered the blocking of VPN services from ISPs, despite there being no solid legislation against such privacy tools.
Venezuela
On June 27, 2018 – According to NGO Access Now, the country’s largest ISP known as “CANTV” blocked the usage of Tor and VPN networks used by Venezuelans.
This was done upon receiving orders from the government, who claim to have created a very simple technique for blocking both tools.
Egypt
After the Egyptian Revolution in 2011, the Government urged the usage of Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) for blocking VPN connections to prevent citizens from accessing restricted content.
The censorship targeted various protocols like PPTP, L2TP, and OpenVPN, so that users cannot access Objectionable Media and Newspapers sites, according to the government.
Unblocking Websites at School/University/Work
In addition to circumventing VPN blocks in various countries, obfuscation does prove extra useful for those wanting to unblock the internet on their school/university/work networks by using a VPN for school.
Since Obfuscation adds a layer of extra encryption cloaked via the HTTPs address, it is impossible for the Network Firewall to block your connection to outside services.
When you use a VPN without obfuscation, the firewall may still get an indication of VPN traffic and block your IP address. Obfuscation prevents this from happening by keeping you anonymous.
The Network Admin will be none the wiser and will not be able to detect your exact IP, also because of the shift in location, so no worrying about getting called into an awkward meeting!
Many people choose to use a VPN on a school or work network in order to access websites that might be blocked by the Network firewall (common examples would be Facebook, YouTube, or gaming sites).
Prevent Bandwidth/Data Throttling from ISPs
It is becoming sort of common for ISPs to slow down networks, despite many countries repelling the Net Neutrality laws, which allows them to charge whatever they want for different services.
For instance, if you want to engage in entertainment, you will have to purchase a separate package to receive more bandwidth/data.
However, despite these changes ISPs have been throttling your bandwidth. Situations are quite worse in places where you have to buy internet access at a hotel.
By activation XOR Obfuscation or a StealthVPN server though, you can avoid the throttling of VPN packets, keeping your speeds at max while maintaining consistency.
Receiving Extra Privacy/Anonymity Online
For the extra privacy-conscious crowd, features like the StealthVPN (Obfuscation), DoubleVPN, Onion over VPN are ways to receive more anonymity and privacy online.
This could be for people who generally are quite secretive, or indulge in matters that require great privacy, which involves sending documents over a private network accessible worldwide.
Once you activate Stealth/Obfuscated Servers, even national spy agencies like the NSA will not be able to identity you, because all traffic passes through the HTTPS tunnel.
Not only does this protect you from secret intelligence agencies, but it also ensures you remain invisible to copyright infringement hunters and cybercriminals.
VPNs that Offer “Obfuscation”
You probably have a good idea now about what “obfuscation” is and how it boosts your privacy online, but what about VPNs that actually offer this feature?
For your convenience, I have listed some of the best providers that offer StealthVPN, obfuscation mode, or selected obfuscation servers in different countries:
NordVPN
Based in Panama (away from Internet Enemy Jurisdictions), NordVPN tends to be an all-rounder VPN service, boasting all relevant advanced features/technologies for boosting your anonymity.
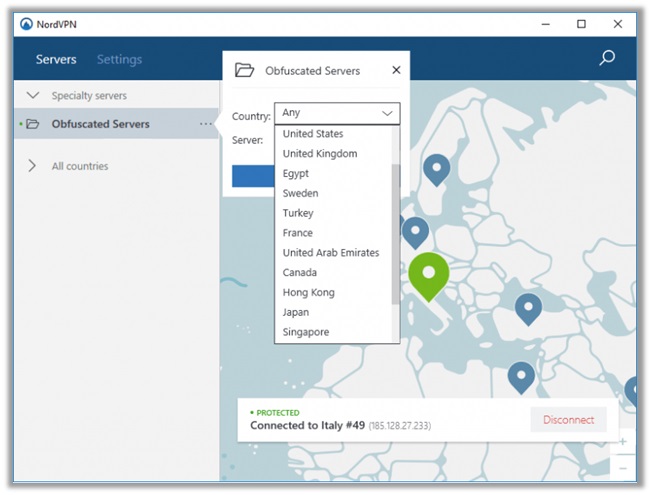
Their obfuscated servers are only available on Windows and Android devices, as I have discussed in this NordVPN Review. Follow the steps below to activate the feature (on Windows):
How to Activate NordVPN Obfuscated Servers
- Download the NordVPN Windows app
- Enter your login credentials to use the VPN
- Go to “Settings” and click on “Advanced Settings”
- Check the “I know what I am doing” box
- Enable the “Obfuscated Servers” option
- Enjoy bypassing VPN Blocks in restricted countries.
ExpressVPN
Headquartered in British Virgin Islands, ExpressVPN is one of the leading privacy tools in the marketplace, offering unmatched security and privacy to users around the world.
They do offer “StealthVPN” only on servers in Hong Kong, specifically designed to defeat censorship in mainland China, but should be useful in other countries where VPNs are blocked.
How to Activate Obfuscation in ExpressVPN
- Download the ExpressVPN Windows app
- Log into your account and enter the activation code
- Connect to servers designated for China Users (ask support team)
- For instance, Hong Kong – 2 uses Obfuscation
- Enjoy bypassing VPN blocks!
VPN. Ac
Based in Romania, VPN. AC is a security-focused provider that delivers good performance and unblocking capabilities. It is among the few services that actually work in China.
The provider does offer obfuscation in their advanced settings, which again transforms VPN traffic to HTTPS traffic to make you invisible to Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) techniques.
How to Activate Obfuscation in VPN. AC
- Download the relevant VPN. AC app for your device
- Log into the application by entering your credentials
- Within the app, go to the “Advanced” menu
- Toggle on “I am in China or other censored country”
- Hit “Connect” and select a server from the “CHINA OPTIMIZED” listing
- Enjoy bypassing VPN blocks and having an unrestricted internet
VPNArea
Based in Bulgaria (away from Internet Enemy Jurisdictions), VPNArea has a Trustpilot rating of 7.9 and is famed for its cheapest vpn pricing and dedicated IPs listing
The provider does offer obfuscation in the form of X-Stunnel servers, meaning they do not use the XOR Obfuscation or Obfsproxy method for transforming VPN traffic into HTTPS.
How to Activate Obfuscation in VPNArea
- Get the suitable VPN application for your device
- Open the app and enter your login details
- Click on “Servers” and select “Special”
- Choose one of the “X-Stunnel” servers available
- Enjoy bypassing VPN blocks in any country!
VyprVPN
Based in Switzerland, VyprVPN is among the only few providers that have been audited by a third-party company, which is available to viewing for the public.
The provider utilizes an advanced obfuscation method in a self-developed protocol known as the “Chameleon Protocol”, which obfuscates all VPN traffic to look like regular HTTPS traffic.
How to Activate Obfuscation in VyprVPN
- Download the VyprVPN app for the relevant device
- Enter your username and password to login
- Click on the “Options/Preferences” option
- Select “Chameleon” for the VPN protocol
- Connect to the faster server available
- Bypass VPN blocks in restrictive countries!
Alternatives to OpenVPN Scramble
There is no doubt that XOR Obfuscation or the security provided by Obfsproxy are exceptional in keeping your identity hidden, scrambling your data and anonymizing all activities.
They hide the fact that your traffic is encrypted, but the lack of obfuscation should not discount an otherwise excellent VPN. Here are some other ways of hiding your VPN traffic:
SSL/TLS Tunnel A.k.a. Stunnel
This is another solid obfuscation tactic that operates by routing your VPN traffic through a secure and encrypted TLS/SSL tunnel, which is used by HTTPS connections.
As such, when OpenVPN connections route through the same encryption, you cannot tell them apart from regular HTTPS traffic, similar to using XOR Obfuscation or Obfsproxy.
Since OpenVPN data itself wraps inside an additional layer of TLS/SSL encryption, even Deep Packet Inspect (DPIs) cannot penetrate this network, keeping you anonymous at all times.
Tor Browser
Short for “The Onion Router” (also depicted in the logo of the browser), Tor was initially developed for the U.S. Navy on 20th September 2002. It featured a global network of servers that allowed people to browse the internet securely and anonymously.
Now, the product has turned towards the non-profit division, spreading the importance of development and research of online privacy tools. It uses a decentralized network, which offers several layers of protection for user data.
It directs internet traffic through an overlay of servers around the world that consist of more than seven thousand relays. This allows for the proper concealing of a users’ location, preventing anyone from monitoring your activity.
SSH Tunnel
SSH Tunnels are another method used by VPNs for covering data with an additional layer of encryption, bypassing filtering services undetected.
It is available in a host of different applications. For example, when you send and receive files via FTP, SSH tunnels securely transfer all data, without monitoring or blockages.
The only problem with SSH tunneling is that it may have an impact on the speeds you receive, hence why they are not a suitable option for those who want to indulge in streaming.
SOCKS5 Proxy (ShadowSocks)
Introduced as a solution for obtaining restriction-free access in countries like China, Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Egypt, and UAE, which use DPI techniques – SOCKS5 proxy uses the Socket Secure 5 protocol.
This protocol is extremely secure and allows for smooth transferring of data using a proxy service, while adding a layer of authentication only the intended user can access.
Not only does this prove useful for users who engage in P2P/file sharing, but it also tends to be more reliable and faster than some of the methods we have explored above.
Wrapping Things Up
In countries with tough internet laws and VPN blocks, features like obfuscation act as a knight in shining armor for privacy-conscious individuals, and those who want to bypass restrictions.
Make sure that you activate this feature, if you reside in a regressive country. The above VPN suggestions should provide you with enough info to select one that best suits your requirements.
Of course, if you have any questions/queries, do not hesitate on commenting below. I will respond personally and provide as much assistance as I can.
Also, help a brother out by sharing this guide with other privacy-focused netizens looking for solutions to boost their anonymity online. Have a lovely day ahead!
